Definitions of Terms for RF and EF Electromagnetic Fields
Definitions of Terms for RF and EF Electromagnetic Fields
Table of Electromagnetic Radiation Frequencies by Type of Source
- POST a QUESTION or COMMENT about the types and frequencies of different radio frequency and other frequencies such as the range of human hearing, radio waves, & the electromagnetic RF spectrum
Definitions & table of signal & other frequencies from lowest to highest:
This article defines and explains electromagnetic field (EMF) or electro-magnetic radiation EMR and related terms such as EMF, radio frequency - RF, hertz or cycles, megahertz, medium frequency MF, very high frequency VHF, ultra high frequency UHF, megahertz MHz, gigahertz GHz, terahertz THz .
InspectAPedia tolerates no conflicts of interest. We have no relationship with advertisers, products, or services discussed at this website.
Definitions & Names of Different Radio Frequency or Electromagnetic Frequency Ranges: RF and EF Electromagnetic Fields
 Before buying test equipment to measure the strength of electromagnetic fields, readers should review this article to be sure that they understand the types of electical fields that exist, the typical sources of different types of electromagnetic fields (power lines, AM and FM radio towers, cell towers, other equipment), and thus the type of test equipment that would be used to assess electrical field strength.
Before buying test equipment to measure the strength of electromagnetic fields, readers should review this article to be sure that they understand the types of electical fields that exist, the typical sources of different types of electromagnetic fields (power lines, AM and FM radio towers, cell towers, other equipment), and thus the type of test equipment that would be used to assess electrical field strength.
Discussed here: What kinds of radio frequency waves are there, what are EMF, RF, hertz, megahertz, MF, VHF, UHF, MHz, GHz, THz ? Definition of ELF EMF VHF UHF - Definitions of electromagnetic frequency ranges & electromagnetic radiation types & sources.
Table of Electromagnetic Radiation Frequencies by Wavelength and Frequency - Table of electromagnetic fields by source type: cell towers, cell phones, power lines, radio towers, home appliances, CRTs, computers, etc. Links to EMF measurement explanations, procedures, worksheets, instruments & advice.
Electromagnetic fields, or EMFs are invisible lines of force created whenever electricity is generated or used. EMFs are produced by power lines, electric wiring, and electric equipment and appliances. The frequency of EMFs is measured in hertz (Hz, or cycles per second).
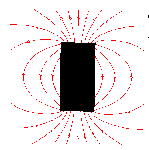
People are exposed to both electric and magnetic fields, but scientists are most concerned about magnetic fields. This fact sheet deals only with magnetic fields that have frequencies near 60 Hz the frequency of electric power in North America.
Static magnetic field around a bar magnet.
Health professionals, epidemiological experts, and in the case of EMF, electrical engineers can offer competent, expert advice which should be considered before any costly or risky actions are taken regarding this or other environmental topics. Use information at this website at your own risk.
Here are simple definitions of terms that you should know if you are concerned with RF or EMF hazards and where they might originate, or how they might be measured
Here we provide a summary of EMF, EMR, and radio frequency cycle rates, and where they are used. Our definitions are arranged in order of increasing frequency or decreasing wave length of electromagnetic signals.
- Hertz - is defined as cycles per second and synonymous with low frequency
- example: 60 Hz - 60 cycles per second is the typical power line distribution EMF frequency in the U.S. One Hz = one cycle per second. - Medium Frequency (MF) - is defined as thousands of cycles per second
- example (530kHz to 1600 kHz) - typical AM radio frequency (your car radio) in thousands of cycles per second. - Very-high VHF and ultra high UHF frequency is defined as millions of cycles per second
- example FM radio, television, digital television, in the MHz range: Megahertz - MHz -
millions of cycles or 1,000,000 cycles per second - NTSC - analog TV
used in most of North America and other countries we're looking in the 1MHz frequency and higher range.
Typically in the 6 to 8 MHz range. TV signals in this frequency range are widespread in North America, and easily penetrate building walls and ceilings. - Extremely high frequency - EHF is defined as billions of cycles per second,
and is the highest radio frequency band, extending from 30 to 300 GHz. or in wavelength size, waves are 1-10 mm or millimeters, also abbreviated MMW or mmW.
Microwaves are an example. - Microwaves
range from 1mm to 1 meter in wavelength, or in a frequency equivalent, from 300 MHz (0.3 GHz) TO 300 GHz. Example: Satellite GPS signals are in this much higher gigahertz range: 1.575 GHz range (easily attenuated by building walls).
Microwave ovens operate in this frequency range when heating food.
Microwaves - is often used in the media as a rather a broad term that encompasses radio or electromagnetic frequencies from roughly 300MHz (300 million waves per second - .1m to 1m in length) to 3GHz (3 billion waves per second - .001 m to 1m in length). - Gigahertz - GHz is defined as billions of cycles per second -
1000 x more than mega, or 1,000,000,000 cycles per second - Microwave towers, UHF and EHF transmission - operate in the 1GHz to 100GHz range. - Terahertz - THz is defined as trillions of cycles per second
- Wavelengths at frequencies still higher than EHF - GHz are referred to as Terahertz radiation, but are more familiarly understood as infrared light.
Still higher frequencies become light visible to the human eye.
One THz is a very high frequency unit of electromagnetic (EM) wave frequency equal to one trillion hertz (10-to-the-12th power Hz) - see our table comparing all of the common Hertz frequency ranges found
at DEFINITIONS of HERTZ, KHz MHz GHz THz .
So a typical low cost instrument suitable to measure power line EMF or Hz is not suitable for TV transmissions measurement in the
MHz range.
Definitions of Electromagnetic Frequencies, EMF, EMR, SAR, RF, Radio Waves, Microwaves
 Definitions of Electromagnetic & Other Radiation Terms
Definitions of Electromagnetic & Other Radiation Terms
Our photo shows a collection of several types of radio transmit/receive antennas in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
[Click to enlarge any image]
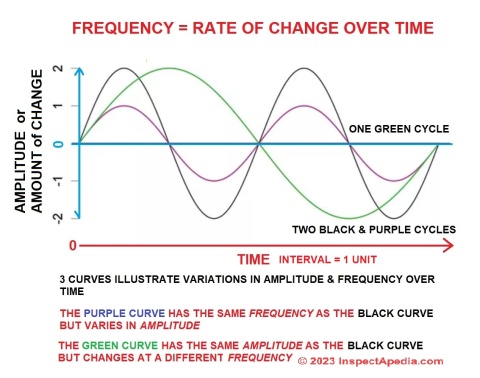
Definition of Frequency
- rate of change over time, or typically, the number of times per second that something happens. For electromagnetic radiation frequency is the oscillation rate or rate of change in frequency as illustrated below.
Definition of Amplitude
- the relative or amount of change in a signal, such as signal strength.
In the sketch below we plot signal amplitude or amount of change on the vertical axis (at left in our drawing) and frequency over time along the horizontal axis (at the bottom of our drawing).
- The green signal curve varies in amplitude between +2 and -2 (shown on the vertical axis) and completes a full cycle just once over the time interval (shown on the horizontal axis). It has a frequency of 1.
- The black signal curve varies in amplitude between +2 and -2 and completes its full cycle twice over the time interval. It has the same amplitude (+/- 2) as the green curve but a frequency of 2.
- The purple signal curve varies in amplitude between +1 and -1 completes a cycle twice over the time interval. It has the same frequency (2) as the purple curve but a different amplitude (+/- 1).
Definition of EMF
- an EMF or electromagnetic field is the field or area of force caused by movement of an electrical charge and containing some amount of electromagnetic energy.
Definition of EMR
- Electromagnetic radiation, or electromagnetic radio frequency radiation EMFR. EMR or electromagnetic radiation is electrical and magnetic energy emitted by various types of energy sources: radio waves, microwaves, light, x-rays, and nuclear energy and sometimes expressed or measured in photons (particles) or as waves (discussed here).
EMR or EM radiation is the result of oscillating electrical and magnetic fields that move as an energy force in wave form through space.
Depending on the wavelength of a particular EMR source, it may be visible to the human eye (in the light spectrum).
While we provide more detailed definitions of types of EMR in this article, roughly EMR is divided according to its wavelength (in order of decreasing wavelength) into electrical energy (such as 60 cycle electrical current in a home, electrons oscillating in an electrical wire), radio waves, microwaves, visible light, ultraviolet light, x-rays, and gamma rays.
The higher the frequency of EMR the shorter is its wavelength. In general, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is synonymous with electromagnetic waves.
Depending on wavelength, energy level, exposure, distance, and other factors, the biological effects of EMR may be heating (warming a chicken leg in a microwave oven), or ionization (knocking an electron off of a molecule to create an ion), to possibly profound effects on molecules or on cells of living tissue.
Definition of Ionizing radiation
- ionizing radiation is electromagnetic waves powerful enough to change (ionize) molecules of a substance (human tissue, for example) that they strike.
Ionizing means creating an "ion" form of a molecule - that is, detaching an electron, converting the molecule to an "ionized" form with a different electrical charge. Ionizing radiation is known to be dangerous to humans and other animals.
It is the energy level of an electromagnetic wave that causes it to become ionizing, not the number of waves that occur. Short-wavelength (high frequency UV [ultra violet], X-rays, gamma rays) radiation is ionizing while low-frequency radiation is not.
Examples of ionizing radiation include high frequency radiation such as from X-rays, gamma rays, or nuclear radiation, alpha rays, beta rays, and neutrons from a nuclear reaction.
Definition of Non-ionizing radiation
- low power non-ionizing radio waves at low levels of transmission power, such as older analog cell phone signals and cell phone radiation.
Definition of SAR & SAR Limits
- Specific Absorption Rate of Radiation - measures the amount of radiation that a human body absorbs from a source such as from a nearby radio transmitting antenna or cellphone (radio receiving antennas do not emit EMF). In the United States the FCC requires that the SAR for cell phones is required to be no more than 1.6 watts per kilogram.
Table of Electromagnetic Radiation Frequencies
The following table summarizes the radiation frequency (cycles per second or Hertz or Hz) and wavelengths (physical length of waves) for various types of electromagnetic radiation sources such as radio waves, microwaves, light, and x-rays. The EM range or EM frequencies extend from a low end of about 1 kHz to 2.4×1023 Hz. - Wikipedia 6/10.
Summary Table of Frequencies of Electromagnetic Radiation |
||
Type of Electromagnetic Radiation SourceArranged in order of increasing frequency (decreasing wavelength) |
Radiation
|
Electromagnetic Frequency (Hertz1)Arranged in order of increasing frequency . Frequency is defined here as the number of waves per second passing a given point or location. |
EMF/ULF: electromagnetic field source from typical residential electrical power Household electrical current, home wiring, electric meters, service entry cables. Power Transmission lines |
Note that power transmission lines and home 120V or 240V appliances operating on 60 cycle alternating current are working at a frequency included in th3e ULF range described just below. | 50 Hz or 60 Hz alternating electrical current See EMF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS & HUMAN EXPOSURE To measure in this range see and also see ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD EMF ELF & RF DETECTION tools
|
Ultra Low Frequency Radiation Used in mining communications below ground, seismic monitoring, secure military communications via ground transmission |
These are the longest electromagnetic waves, geomagnetic pulsations, micropulsations. Wavelength may be 5000 x radius of the earth | 1 Hz up to 1kHz Most sources: under 300 Hz Other sources:
|
Very Low Frequency Radiation VLF Used for radio navigation, submarine communication, geophysical surveys, some natural emissions |
10,000 meter band, Myriameter wave |
2 kHz up to 30 kHz Other sources: Myriameter band |
| Low Frequency Radiation - range of human hearing | Frequency range of human hearing, in sound pressure variations per second | 12 Hz up to 20 kHz or about 15 to 20,000 cycles. [4] That is, from about 12 cycles per second up to 20,000 cycles per second. Some sources place the human auditory threshold at 3 cycles/sec. Note that sound waves traveling air are in essence moving the air against the eardrum in an animal's ear - these are audio waves and not a form of electromagnetic radiation. |
Low Frequency Radiation Used for aircraft navigation, LORAN, weather, time signals |
1,000 meter band, Kilometer wave |
30 kHz up to 300 kHz AM broadcasting in Europe & other areas Longwave band, kilometer band |
Medium Frequency MF AM and other Radio broadcasting, electrons oscillating in an antenna. |
103 down to 10-1 100 meter band, Hectometer wave
|
300 kHz up to 3 MHz - 106 up to 109 530 kHz to 1600 kHz AM radio Broadcast band |
High Frequency HF AM Radio broadcasting, electrons oscillating in an antenna. |
100 meters down to one meter - 103 down to 10-1 (one meter) 10 meter band, Decameter wave |
3 MHz up to 30 MHz Decameter band To measure in this range see |
| Very High Frequency VHF FM Radio & TV Waves FM Radio and TV broadcasting, electrons oscillating in an antenna. |
1 meter band | 30 MHz up to 300 MHz - |
Ultra High Frequency UHF Radio and TV broadcasting, Satellite communications; * The current US exposure standard for cell site radiation in the US is 580-1000 microwatts per square centimetre. |
1 meter down to 10 cm |
300 MHz up to 3 GHz - Cordless phones - roughly 100-900 MHz Radar - marine, low end units operate at 3 GHz To measure in this range see |
Extremely High Frequency EHF Molecular rotation, plasma oscillation |
10-1 down to 10-4 meters | 30-300 Gigahertz GHz - 109 up to 1012 Marine Radar operates typically from about 2 GHz up to 10 GHz To measure in this range see |
Infrared Molecular rotation, plasma oscillation |
10-4 down to 0.7 ×10-6 | Terahertz THz - 1012 up to 1015 |
Visible light Molecular electron excitation - interaction with human eye retinal cells |
0.7 ×10-6 down to 0.4 ×10-6 | 1015 |
Ultraviolet light Molecular & atomic electron excitation |
0.4 ×10-6 down to 10-8 | 1015 up to 1017 |
X-rays Excitation & ejection of core atomic electrons |
10-8 down to 10-12 | 1017 up to 1021 |
Notes to the table above
- See our table comparing different Hertz frequency ranges at Hertz - Definitions of KHz MHz GHz THz
- How do we get to "approximately the speed of light" for data in the electromagnetic radiation wavelengths and frequencies above? For a given electromagnetic wave, multiplying the wavelength by wave frequency for any given electromagnetic signal will equal to roughly the speed of light.
- Definitions: One Hz or Herz = one cycle per second or one "wave" per second passing a given point
One kHz or Kilohertz = one thousand cycles per second or 1000 waves per second
One MHz or Megahertz = one million waves or cycles per second
One GHZ or Gigahertz = one billion waves or cycles per second passing a given point - Range of human hearing, citations:
- Cutnell, John D. and Kenneth W. Johnson. Physics. 4th ed. New York: Wiley, 1998: 466.
- "Body, Human." The New Book of Knowledge. New York: Grolier, 1967: 285.
- Caldarelli, David D. and Ruth S. Campanella. Ear. World Book Online Americas Edition. 26 May 2003.
Cellphone Radiation Information & Reducing Cellphone EMR Exposure
Please see our full article on this topic found
at CELLPHONE RADIATION HAZARDS.
Excerpts from that article are below
Readers of this article should also
see EMF RF FIELD & FREQUENCY DEFINITIONS
and EMF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS & HUMAN EXPOSURE
Definition of cellphone radiation - cellular telephones, because they include a radio transmitter, emit electromagnetic fields (EMF, or EMR).
In the United States the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) specifies the allowable limits of cell phone radiation.
A possible concern is the exposure of the human ear and brain to cellphone radiation, especially as newer digital cell phones operate at higher power and at frequencies in the 1800-2000 MHz range.
Present cell phones may exceed the FCC EMR limit that was set when most cell phones were analog in signal design and emitted lower-strength EMFs in the 800-900 MHz range.
Scientific research on possible health hazards from cellphone use to date (2010) has produced inconclusive and conflicting results, varying by study. According to an article in June 2010 the New York Times,
Both the National Cancer Institute and the F.C.C. [Federal Communications Commission] say that there is no scientific evidence that wireless phones are dangerous, but each agency continues to monitor continuing medical studies.
What type of radiation is emitted by a cellphone? older cell phones emit and receive low level radio frequency waves from 200 MHz to more than 800 MHz. Newer cell phones operate in the 900 MHz to 2.4 GHz or more (approaching the power and frequency of microwaves and infrared waves).
Transmission of signals in the cellphone range are also referred to as UHF or Ultra High Frequency Signals.
Base to Mobile and Mobile to Base Cellphone Frequencies May Differ
It is worth noting that typically the signals that pass between a cell phone and a cell tower are at different frequency ranges depending on the direction of transmission.
For example, a cell phone may transmit from the phone to the cell tower at around 800 MHz, while the tower transmits back to the cellphone at around 1800 MHz.
Because the power level of a cellphone while it is transmitting is very small compared to the powe of the cell phone tower when it is transmitting, that means that the stronger of the two cell phone frequencies is the tower transmission signal.
In reading various publications that discuss cell phone frequencies, you may read the cellphone transmit frequency as "mobile to base" and the tower transmit frequency from tower to cellphone as "base to mobile".
Cellphone Abbreviations and Terms - What Frequencies Your Cellphone Uses Depend on Your Wireless Carrier as Well as the Phone Itself
AMPS - Advanced Mobile Phone Service - Cell phone industry standard since 1978
Analog service: radio signals modulated to carry information in a continuous signal, like FM radio. Receiver and transmitter use the same frequency.
Digital cell phone service: radio signals are digitized using a binary code (0's and 1's) to convert speech (or any signal sent to or received from a cellphone) to binary data. In the U.S there are 3 wireless technologies: CDMA, TDMA, and GSM.
And of course 1G; 2G; 3G; 3.5G; 4G; 4.5G; and the newest, 5G technology under development in 2019.
- TDMA - Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA IS-54) or Digital Amps or D-Amps - since 1994, operates in North America in the 800 MHz band and in the 1900 MHz band, used by AT&T, Bell South, Southwestern Bell.
- CDMA - Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA IS-95), in use since th3 1940's, operates at both 800 MHz and 1900 MHz bands, used in the U.S. primarily by Verizon Wireless, and Sprint/Nextel, though CDMA is also used by other carriers including Cricket, MetroPCS, and U.S. Cellular.
CDMA was a proprietary standard developed by Qualcomm in the U.S. EV-DO being developed for CDMA networks (CDMA2000) provides faster data download speeds, similar to DSL in speed. - GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications - an improved version of TDMA, adopted first in Europe by 1987, uses wider signal channels (200 KHz) than TDMA. GSM 1900 is used by Aerial, Bell South, Microvcell, Omnipoint, Pacific Bell, Spring Spectrum, Western Wireless. EDGE being developed for GSM networks provides faster data download speeds, similar to DSL in speed.
- 800 MHz band authorized by the U.S. FCC in 1987 for cellphone use.
PCS - Personal Communications Services - 1.9 GHz all digital transmission and reception authorized by the U.S. FCC
SIM cards - Subscriber Identity Module cards are small printed circuit boards that contain individual cell phone account information and that are inserted into GSM phones (in the U.S.).
Because the SIM card contains the user information, cellphones that accept SIM cards become generic - you can move your cell phone account to a new telephone by inserting your SIM card into a new phone, or you can change your cell phone to a different service provider (and telephone number) by buying and inserting a different SIM card into your existing GSM phone.
Reader Comments, Questions & Answers About The Article Above
Below you will find questions and answers previously posted on this page at its page bottom reader comment box.
Reader Q&A - also see RECOMMENDED ARTICLES & FAQs
On 2021-03-19 - by (mod) - don't panic: remembrer that strength of an EMF falls off with the square of the distance.
@Jim Navotney,
Thank you again for the comment.
In general it's true that unless you're sleeping with your head in the microwave you don't need to be afraid of it.
I have found a few unusual cases in which there was a very strong electrical field next to the headboard of a bed because of the routing and positioning of an electric meter in the service entrance cable.
There are photos of that in this article series. But it's quite unusual.
The basic point is that the strength of the field falls off with the square of the distance.
On 2021-03-19 by Jim Navotney
@Lei Chu, It sounds like some subsonic sound is in your area and the air conditioner box is the perfect size to be resonant at that frequency.
I would try to isolate the unit with rubber washers or foam rubber seal.
Billions of dollars have been made off the public by creating fear over EMF and RF exposure and none are true.
You are in fact bathed in RF and EMF 24 hours a day everywhere on the planet and HAVE been since the first radio and radar transmitter hit the air in the 30s.
Today thousands of satellites are directly over your head and tens of thousands of TV, FM, AM, marine, police, aircraft, paging, ham radio, cellular, GPS, and wifi transmitters are all around you 24-7.
The Chinese have sold millions of their cheap "EMF" detectors to the tin foil hat crowd and the great 5G hoax has caused the gullible to burn and destroy cell and 911 towers around the world as a direct result of their sale.
Unless you use your power meter or wifi router as your pillow, you have zero to fear
On 2020-07-23 by Lei Chu
I recently have a big problem with Metal objects. Especially when the new big steel made air condition compressor box (80*80*90 cm) galvanized
steel is installed.
Only this brand Goodman, not others. This metal radiate out big metal kind of sharp noise and sound (not when it is turned on)
but when it is still. Maybe I got some super sense. But it exists. (our old brand does not do like this, nor our neighbor's Lennox brand). I am talking about when the box is in a still state.
So, it comes to the EMF, EMF only happen when the electricity current is on.
So, I think it deals with the OBJECT VIBRATION things.
Actually I had discussed this with Texas State radiation center and one of them did come with a Geiger detector . And this box does not have reaction to it.
But for EMF, I did not buy one yet to test. But I think if I don't feel anything around a microwave, then this steel airconditioner box probably does not belong to that category.
But I can feel wifi's EMF though. And the air conditioner compressor's box (steel ) radiation (i call it this) strength is about 10 times bigger . So
my body is like a sensor.
MY Problem is: How do I block this metal thing?
(I actually bought lead sheet to cover inside of the wall next to this box installed outside) but it does not stop the noise sound (when the box is not turn on).
So it is of object vibration then.
What can block it?
any detector to test this kind of object vibration?
(Not every steel object has the same wave. I did not study physics, I only sensed it. for building with bad steel , objects....etc)
Please advise me , thank you.
Lei Chu
On 2017-02-01 - by (mod) - give me the effects of electromagnetic frequencies
Anon
In the article above in the table, OR in the Article INDEX given at More Reading just above, see this article
EMF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS & HUMAN EXPOSURE
On 2017-02-01 by Anonymous
give me the effects of electromagnetic frequencies
On 2016-10-16 by isreal
I would really like to know the amplitude of all the terms above,id really appreciate it,cause am lost.
On 2016-09-07 - by (mod) -
Mom,
From e-text I cannot guess what your neighbor is doing nor what are its effects.
I can say that exposure to an electromagnetic field, such as emitted by power lines, would not be expected to make your ears pop.
Watch out: Someone who's not expert at detecting different types of electrical fields is at risk of buying a "test device" that has nothing to do with what's actually going on at a property. It's sort of a stab in the dark.
You would be best served by your local authorities, building department, electrical inspector, building code officials or health department.
On 2016-09-07 by MomofTwo
I need help with this and you seem like you know whats going on and I am past the point of sounding crazy. I am worried for my children and myself The neighbor seems to be using some sort of device that when he turns it on it causes our ears to pop from the pressure, head pain, and sometime nausea.
What I do know is he has a primitive recording studio in his house and after playing a measly 15 hertz mosquito video from YouTube on a big blue speaker, on the advice of a friend that understands electronic equipment.
The neighbor freaked out and ran around his yard pulling cables and at least 4 or 5 microphones out of shrubs and trees. However, when the FBI didn't show up we watched him install those items back in diverse places around his property.
We watched him on our security cameras which we had installed because we suspected something seriously wrong going on. In retaliation for playing the 15 hrtz so that it annoyed him while he tries to listen in on our boring conversations, he has begun to harass us with whatever he is using. I am wondering if he didn't buy a RF Generator and amplified it while using some type of directional equipment.
We are trying to figure out and collect information before we contact the proper authorities. However, it sounds crazy to say something the jerk is doing is hurting our ears, but no, you can't hear it.
I already purchased the, Hf35c Rf Analyze (800mhz - 2.5 Ghz) -, but think it wont pickup what he is broadcasting because his frequency isn't as high as the equipment tests for. It arrives next week. Also I forgot to mention that we keep a radio on and tuned to the NOAH channel.
When we feel the ear pressure and pain, the NOAH weather channel fades to white noise. You can tell when he turns it off as the channel comes back in and you can once again hear the NOAH broadcast.
However, I think he is changing the frequency since for the first time yesterday I noticed the security cameras which we display over a regular flatscreen, not smart, TV, closed circuit, the screen on the TV was exhibiting interference. Later in the day when I looked again it was gone. Had not noticed that before. I know it sounds crazy, but any advice would be appreciated.
On 2016-03-07 - by (mod) -
Marine Radar:
To provide space for answering in more detail I've repeated your question and posted our answer at
RF RADIO FREQUENCY DETECTION METERS - https://inspectapedia.com/emf/Radio_Frequency_RF_Measurement_Tools.php
Please let me know if questions remain
On 2016-03-07 by Marine Radar Units
I am a lock and Dam Operator. Recently I was told to start having the pilots of these tow boats put there radars in stand by mode. If they are on, lime they have been for the last 6 years I have been working that they pose a heath hazard to us since we normally work with in 10 foot of these things and are pretty much at eye level with them.
I read the above article in hopes of finding a tool to measure the amount of radiation we are exposed to but didn't find what I was looking for. I may have missed it. Can you help me out. Thanks
Question: is it unhealthy to live near an AM radio tower?
Do you think it is a health hazard for a sensitive person to live near AM radio towers that emit 5,400-6,000 mV/m? The AM station frequency is 1260. Thanks. - Sarah 8/3/2011
Reply:
Sarah AM radio stations transmit medium frequency radio waves, not low frequency EMF; The U.S. FCC reports no health hazard from exposure to AM radio transmissions from RF (radio frequency) transmissions.
But at least some research shows that exposure to high levels of RF may be harmful. Because the jury is likely to remain out on this topic for some time, a reasonable approach is that of "prudent avoidance" - meaning that you would take reasonable steps to avoid prolonged exposure to high levels of EMF or RF energy but you would not panic, spend thousands of dollars on questionable "magic bullet" remedies, etc.
You can start by determining just what your exposure is by duration, distance, and signal strength. As we describe in these articles, inexpensive RM measuring equipment is available from a number of manufacturers.
And while working to stay healthy and safe, keep hazards in their proper perspective. Falling down the stairs (the most common accident) or failing to wear a seat belt, or smoking, are more immediate health hazards that are easy to avoid.
Question: reader fears people are being decimated by EMF
I would particularly like to know how you presume your enviro-scare bell curve has any bearing on reality given that people are likely to be debilitated or decimated, keeping the alarms on environmental hazards muted. Please forward me a copy of this e-message with your response to it. - mungai.annie@yahoo.com 12/19/2012
Reply: clarifying the definition of Enviro-Scare
Annie, your question is unfortunately based on what appears to be your own presumption of level of risk, and sadly, reports that "people are likely to be decimated" - which I understand to mean "slaughtered wholesale" (a stunning remark for which you offer no authoritative citations regarding electromagnetic fields).
Compounding these errors you presume that we are motivated to "mute environmental hazards" - an incorrect conclusion regarding our concern for public safety that is readily apparent from reading any of the thousands of articles found at InspectApedia.com.
Lastly, you have perhaps missed the point of the bell curve that is used to desribe Enviro-Scare, so let me try to clarify that topic. Enviro-Scare refers to the observation, made over decades, that regardless of whether or not a particular environmental hazard is found to be real or imagined, the level of public fear about the hazard follows the pattern of a bell curve, increasing as news reaches the public, reaching a peak, and eventually falling off to near zero, independent of the actual level of risk.
Annie, it is indeed important to take real risks seriously, and at the same time, to set our priority of attention to be sure that we address both great and immediate risks first, as well as subtle and longer term risks such as those that may be present from various environmental contaminants.
In other words, if you break your neck falling down the stairs, the fact that you were exposed to DES as a child in utero will pale in significance.
We are dedicated to making our information as accurate, complete, useful, and unbiased as possible and are so we very much welcome critique, questions, or content suggestions for our web articles.
...
Continue reading at DEFINITIONS of HERTZ, KHz MHz GHz THz or select a topic from the closely-related articles below, or see the complete ARTICLE INDEX.
Or see these
Recommended Articles
- CELL PHONE RADIATION
- DEFINITIONS of EMF RF FIELD & FREQUENCY
- DEFINITIONS of HERTZ, KHz MHz GHz THz
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD EMF ELF & RF DETECTION
- EMF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS & HUMAN EXPOSURE
- EMF CANCER SCARE
- EMF CANCER RISK
- EMF/EMR MEASUREMENT OVERVIEW
- EMF LOCAL SOURCES MAY EXCEED POWER LINE STRENGTH
- EMF MEASUREMENT DISTANCE AFFECTS STRENGTH
- EMF MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENTS
- EMF MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT ACCURACY
- EMF MEASUREMENT INSTRUMENT USE TIPS
- EMF MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES
- EMF MEASUREMENT STEP BY STEP
- EMF REFERENCES
- EMF SURVEY PROCEDURE
- EMF SURVEY REPORT INTERPRETATION
- EMF WORKSHEET for EMF MEASUREMENTS
- EMF WORKSHEET Example
- EMF WORKPLACE EXPOSURE
- ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARDS at BUILDINGS - home
- ENVIRO-SCARE - PUBLIC FEAR CYCLES
- HAZARD vs RISK
- RF RADIO FREQUENCY DETECTION METERS
Suggested citation for this web page
DEFINITIONS of EMF RF FIELD & FREQUENCY at InspectApedia.com - online encyclopedia of building & environmental inspection, testing, diagnosis, repair, & problem prevention advice.
Or see this
INDEX to RELATED ARTICLES: ARTICLE INDEX to BUILDING ENVIRONMENT
Or use the SEARCH BOX found below to Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Ask a Question or Search InspectApedia
Try the search box just below, or if you prefer, post a question or comment in the Comments box below and we will respond promptly.
Search the InspectApedia website
Note: appearance of your Comment below may be delayed: if your comment contains an image, photograph, web link, or text that looks to the software as if it might be a web link, your posting will appear after it has been approved by a moderator. Apologies for the delay.
Only one image can be added per comment but you can post as many comments, and therefore images, as you like.
You will not receive a notification when a response to your question has been posted.
Please bookmark this page to make it easy for you to check back for our response.
Our Comment Box is provided by Countable Web Productions countable.ca
Citations & References
In addition to any citations in the article above, a full list is available on request.
- "San Francisco Law Will Make Cellphone Retailers List Radiation Rate", Jesse McKinley, The New York Times, 16 June 2010 p. A14.
- ANSI-C95.1, 1982, American National Standards Institute. American national standard safety levels with respect to human exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields, 300 kHz to 100 Ghz. New York: IEEE.
- Elliott P, Toledano MB, Bennett J, et al. Mobile phone base stations and early childhood cancers: case-control study. BMJ. 2010;340:c3077. [Epub ahead of print]
- IEEE-C95.1, 1991, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. Safety levels with respect to human exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields, 3 kHz to 300 Ghz. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE.
- IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. Human exposure to RF emissions from cellular radio base station antennas; Washington, DC: 1992.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA Consumer magazine November-December 2000 Telephone: (888) INFO-FDA http://www.fda.gov (Under "c" in the subject index, select Cell Phones>Research.)
- U.S. Federal Communications Commission 445 12th St. S.W. Washington, D.C. 20554 Telephone: (888) 225-5322 http://www.fcc.gov/oet/rfsafety
- Independent Expert Group on Mobile Phones http://www.iegmp.org.uk/
- Royal Society of Canada Expert Panel on Potential Health Risks of Radiofrequency Fields from Wireless Telecommunications Devices 283 Sparks Street Ottawa, Ontario K1R 7X9 Canada Telephone: (613) 991-6990
- World Health Organization Avenue Appia 20 1211 Geneva 27 Switzerland Telephone: 011 41 22 791 21 11 http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs193/en/
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection c/o Bundesamt fur Strahlenschutz Ingolstaedter Landstr.1 85764 Oberschleissheim Germany Telephone: 011 49 1888 333 2156 http://www.icnirp.de/
- American National Standards Institute 1819 L Street, N.W., 6th Floor Washington, D.C. 20036 (202) 293-8020 http://www.ansi.org/
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements 7910 Woodmont Avenue, Suite 800 Bethesda, MD 20814-3095 Telephone: (301) 657-2652 http://www.ncrponline.org/
- Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Committee on Man and Radiation (COMAR), of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers http://ewh.ieee.org/soc/embs/comar/
References for Electromagnetic Fields and Cancer Risk/Carcinogenicity
- Electric Power Lines, Electromagnetic Fields, Cancer Risk, & "Enviro-Scare" - The Normal Curve Cycle of Public Fear About Environmental Issues - online document by DF
- A Procedure for Measuring EMF electromagnetic fields online document by DF
- "Questions and Answers about Biological Effects and Potential Hazards of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields", Federal Communications Commission, Office of Engineering and Technology, US FCC, OET Bulleting 56, 4th Edition, August 1999
" Many consumer and industrial products and applications make use of some form of electromagnetic energy. One type of electromagnetic energy that is of increasing importance worldwide is radiofrequency (or "RF") energy, including radio waves and microwaves, which is used for providing telecommunications, broadcast and other services. In the United States the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) authorizes or licenses most RF telecommunications services, facilities, and devices used by the public, industry and state and local governmental organizations. Because of its regulatory responsibilities in this area the FCC often receives inquiries concerning whether there are potential safety hazards due to human exposure to RF energy emitted by FCC-regulated transmitters. Heightened awareness of the expanding use of RF technology has led some people to speculate that "electromagnetic pollution" is causing significant risks to human health from environmental RF electromagnetic fields. This document is designed to provide factual information and to answer some of the most commonly asked questions related to this topic." - original source: U.S. Federal Communications Commission Office of Engineering and Technology, http://www.fcc.gov/Bureaus/Engineering_Technology/Documents/bulletins/oet56/oet56e4.pdf - "Magnetic Field Exposure and Cancer: Questions and Answers [ copy on file as /emf/EMF_Fact_Sheet_NCI_NIH.pdf ] - ," National Cancer Institute, U.S. National Institutes of Health, web search September 2010, original source: http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/Risk/magnetic-fields
makes these five key points about EMF- Electric and magnetic fields (EMF) are areas of energy that surround any electrical device. EMFs are produced by power lines, electrical wiring, and appliances (see Question 1).
- Electric fields are easily shielded or weakened by walls and other objects, whereas magnetic fields are not. Since magnetic fields are more likely to penetrate the body, they are the component of EMFs that are usually studied in relation to cancer (see Question 1).
- Overall, there is limited evidence that magnetic fields cause childhood leukemia, and there is inadequate evidence that these magnetic fields cause other cancers in children (see Question 2).
- Studies of magnetic field exposure from power lines and electric blankets in adults show little evidence of an association with leukemia, brain tumors, or breast cancer (see Question 3).
- Past studies of occupational magnetic field exposure in adults showed very small increases in leukemia and brain tumors. However, more recent, well-conducted studies have shown inconsistent associations with leukemia, brain tumors, and breast cancer (see Question 4).
- EMF RF FIELD & FREQUENCY DEFINITIONS RF and EMF measurement tools need to be properly chosen to measure the particular type and frequency of RF or EMF signal that is of interest. See EMF RF FIELD & FREQUENCY DEFINITIONS for a simple explanation of different types of radio frequency (RF) and electromagnetic frequency (EMF) types and where they are found.
- "Evaluation of Potential Carcinogenicity of Electromagnetic Fields," EPA Report #EPA/600/6-90/005B October 1990. EPA: 513/569-7562.
- "Biological Effects of Power Frequency Electric and Magnetic Fields" background paper, prepared as part of OTA's assessment of "Electric Power Wheeling and Dealing: Technological Considerations for Increasing Competition," prepared for OTA by Indira Nair, M. Granger Morgan, H. Keith Florig, Department of Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213
- "Biological Effects of Power Line Fields," New York State Powerline Project. Scientific Advisory Board Final Report, July 1, 1987.
- "Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) Fields," Environmental Health Criteria 35. World Health Organization, Geneva, 1984.
- "Electric and Magnetic Fields at Extremely Low Frequencies: Interactions with Biological Systems. In: Non ionizing Radiation Protection, World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe, Copenhagen, 1987.
- "Electric and Magnetic Fields from 60 Hertz Electric Power: What do we know about possible health risks?," Department of Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213 1989.
- "Electromagnetic Fields Are Being Scrutinized for Linkage to Cancer," Sandra Blakeslee, New York Times, Medical Science section, April 2, 1991
- Our recommended books about building & mechanical systems design, inspection, problem diagnosis, and repair, and about indoor environment and IAQ testing, diagnosis, and cleanup are at the InspectAPedia Bookstore. Also see our Book Reviews - InspectAPedia.
- In addition to citations & references found in this article, see the research citations given at the end of the related articles found at our suggested
CONTINUE READING or RECOMMENDED ARTICLES.
- Carson, Dunlop & Associates Ltd., 120 Carlton Street Suite 407, Toronto ON M5A 4K2. Tel: (416) 964-9415 1-800-268-7070 Email: info@carsondunlop.com. Alan Carson is a past president of ASHI, the American Society of Home Inspectors.
Thanks to Alan Carson and Bob Dunlop, for permission for InspectAPedia to use text excerpts from The HOME REFERENCE BOOK - the Encyclopedia of Homes and to use illustrations from The ILLUSTRATED HOME .
Carson Dunlop Associates provides extensive home inspection education and report writing material. In gratitude we provide links to tsome Carson Dunlop Associates products and services.